Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Feature data-type in tree-based models
Tree-based models in emlearn supports both float and integer datatypes for the feature datatype. This example illustrates how this can impact model size.
import os.path
import emlearn
import numpy
import pandas
import seaborn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
try:
# When executed as regular .py script
here = os.path.dirname(__file__)
except NameError:
# When executed as Jupyter notebook / Sphinx Gallery
here = os.getcwd()
Train a RandomForest model
Key thing is to transform the data into integers that fit the
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, StratifiedKFold
def train_model(data):
label_column = 'label'
feature_columns = list(set(data.columns) - set([label_column]))
X = data[feature_columns]
Y = data[label_column]
# Rescale and convert to integers (quantize)
# Here everything is made to fit in int8, the smallest representation
# it may be needed to adapt to larger ones, such as uint16
X = (MinMaxScaler().fit_transform(X) * 127).astype(int)
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10, max_depth=10, random_state=1)
# sanity check performance
cv = StratifiedKFold(5, random_state=None, shuffle=False)
scores = cross_val_score(model, X, Y, cv=cv)
assert numpy.mean(scores) >= 0.60, numpy.mean(scores)
model.fit(X, Y)
return model
from emlearn.examples.datasets.sonar import load_sonar_dataset
data = load_sonar_dataset()
model = train_model(data)
Measure how feature datatype impacts program size
We are testing here on the AVR8 platform, which has no floating point unit (FPU) Other platforms may show different results.
from emlearn.evaluate.size import get_program_size, check_build_tools
def check_program_size(dtype, model, platform, mcu):
model_name = 'sizecheck'
features_length = model.estimators_[0].n_features_in_
model_enabled = 0 if dtype == 'no-model' else 1
if dtype == 'loadable':
dtype = 'float'
method = 'loadable'
else:
method = 'inline'
if model_enabled:
# Quantize with the specified dtype
c_model = emlearn.convert(model, dtype=dtype, method='loadable')
model_code = c_model.save(name=model_name, inference=[method])
if method == 'loadable':
# XXX: the cast to float is wrong. Will crash horribly during execution
# Only works for size estimation
model_code += f"""
int {model_name}_predict(const {dtype} *f, int l) {{
return eml_trees_predict(&{model_name}, (float *)f, l);
}}"""
else:
model_code = ""
test_program = \
f"""
#include <stdint.h>
#if {model_enabled}
{model_code}
static {dtype} features[{features_length}] = {{0, }};
#endif
int main()
{{
uint8_t pred = 0;
#if {model_enabled}
pred = {model_name}_predict(features, {features_length});
#endif
int out = pred;
return out;
}}
"""
data = get_program_size(test_program, platform=platform, mcu=mcu)
return pandas.Series(data)
def run_experiment(model, platform, mcu):
results_file = os.path.join(here, f'trees-feature-quantization-{platform}+{mcu}.csv')
# check if AVR build tools are present. If not, just load results from a file
missing_tools = check_build_tools(platform)
if missing_tools:
print(f"WARNING: Compiler toolchain for platform '{platform}' not found. Loading cached results")
results = pandas.read_csv(results_file)
else:
experiments = pandas.DataFrame({
'dtype': ('no-model', 'loadable', 'float', 'int32_t', 'int16_t', 'int8_t', 'uint8_t'),
})
results = experiments['dtype'].apply(check_program_size, model=model, platform=platform, mcu=mcu)
results = pandas.merge(experiments, results, left_index=True, right_index=True)
results = results.set_index('dtype')
# subtract overall program size to get only model size
results = (results - results.loc['no-model'])
results = results.drop(index='no-model')
# add identifying information
results['platform'] = platform
results['cpu'] = mcu
results = results.reset_index().set_index(['platform', 'cpu', 'dtype'])
results.to_csv(results_file)
print("Ran experiments. Results written to", results_file)
return results
platforms = pandas.DataFrame.from_records([
('avr', 'atmega2560'),
('arm', 'Cortex-M0'),
('arm', 'Cortex-M4F'),
], columns=['platform', 'cpu'])
results = pandas.concat([run_experiment(model, platform=row.platform, mcu=row.cpu) for idx, row in platforms.iterrows()])
print(results)
WARNING: Compiler toolchain for platform 'avr' not found. Loading cached results
WARNING: Compiler toolchain for platform 'arm' not found. Loading cached results
WARNING: Compiler toolchain for platform 'arm' not found. Loading cached results
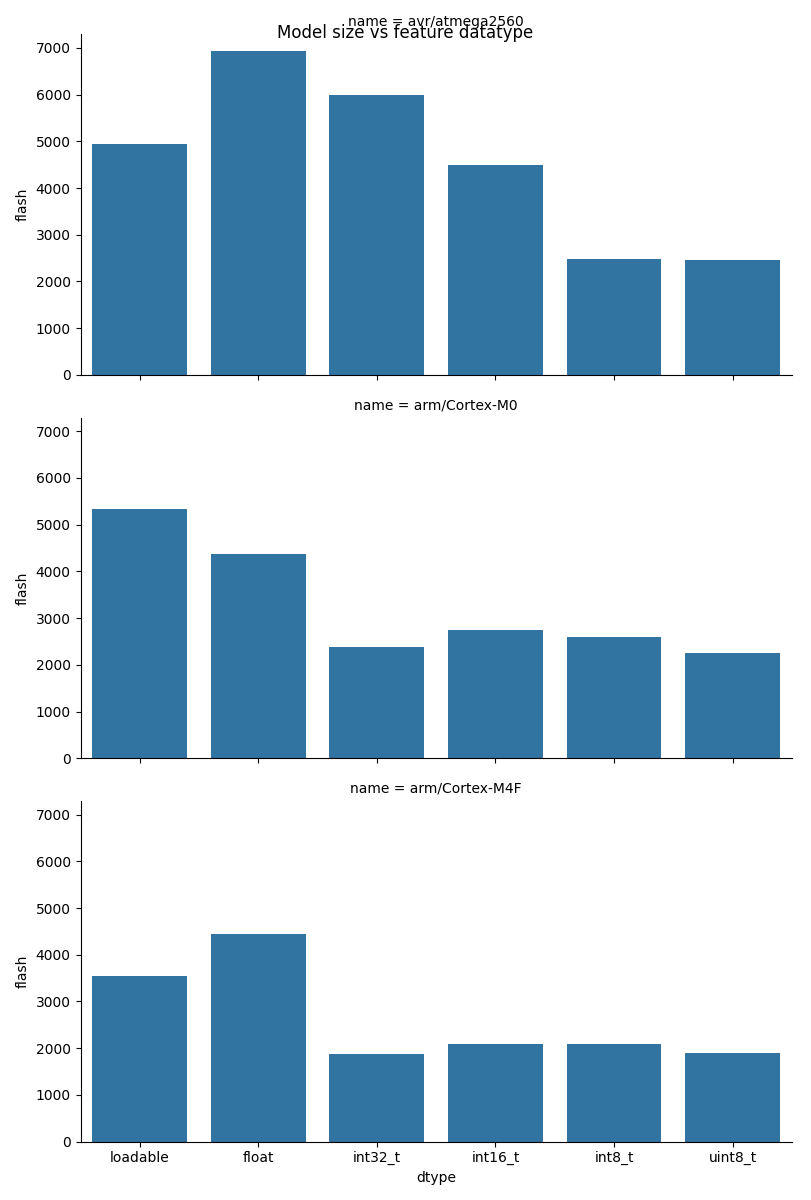
platform cpu dtype flash ram
0 avr atmega2560 loadable 4934 2472
1 avr atmega2560 float 6944 240
2 avr atmega2560 int32_t 6000 240
3 avr atmega2560 int16_t 4496 120
4 avr atmega2560 int8_t 2480 60
5 avr atmega2560 uint8_t 2466 60
0 arm Cortex-M0 loadable 5336 264
1 arm Cortex-M0 float 4372 240
2 arm Cortex-M0 int32_t 2380 240
3 arm Cortex-M0 int16_t 2752 120
4 arm Cortex-M0 int8_t 2600 60
5 arm Cortex-M0 uint8_t 2244 60
0 arm Cortex-M4F loadable 3544 264
1 arm Cortex-M4F float 4444 240
2 arm Cortex-M4F int32_t 1880 240
3 arm Cortex-M4F int16_t 2080 120
4 arm Cortex-M4F int8_t 2080 60
5 arm Cortex-M4F uint8_t 1892 60
Plot results
There can be considerable reductions in program memory consumption by picking a suitable datatype for the platform.
def plot_results(results):
results = results.reset_index()
results['name'] = results.platform + '/' + results.cpu
g = seaborn.catplot(data=results,
kind='bar',
y='flash',
x='dtype',
row='name',
height=4,
aspect=2,
)
fig = g.figure
fig.suptitle("Model size vs feature datatype")
return fig
fig = plot_results(results)
fig.savefig('example-trees-feature-quantization.png')
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.575 seconds)