Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
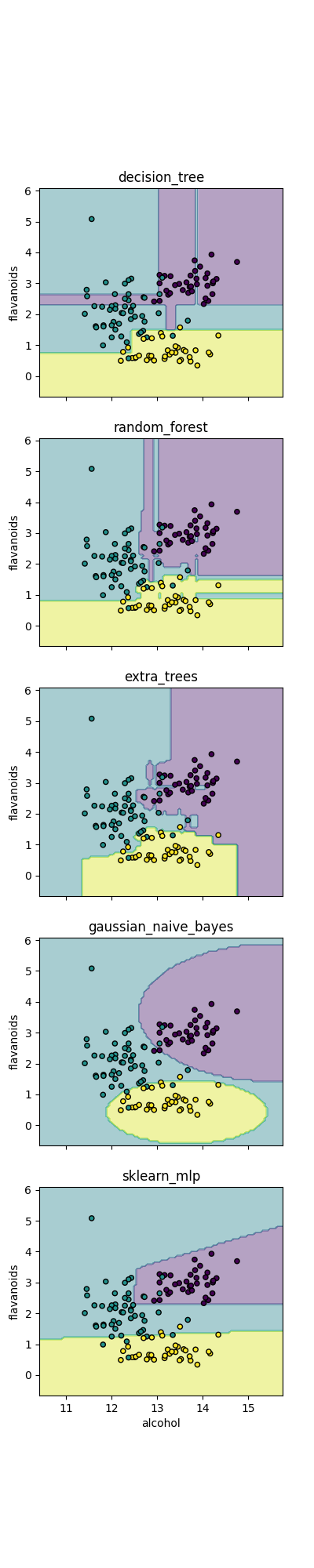
Classifier comparison
Simple demonstration of the different implemented classifiers in emlearn
import os.path
import emlearn
import numpy
import pandas
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn
try:
# When executed as regular .py script
here = os.path.dirname(__file__)
except NameError:
# When executed as Jupyter notebook / Sphinx Gallery
here = os.getcwd()
Create dataset
Using a simple multi-class dataset included with scikit-learn
def load_dataset():
from sklearn import datasets
data = datasets.load_wine(as_frame=True)
df = data.data.copy()
df.columns = data.feature_names
df['target'] = data.target
return df
dataset = load_dataset()
Correctness checking
Compare predictions made by converted emlearn C model with those of the trained Python model
def check_correctness(out_dir, name, model_filename, test_data, test_predictions, feature_columns):
test_res = numpy.array(test_predictions).flatten()
test_dataset = "\n".join([
emlearn.cgen.array_declare(f"{name}_testset_data", dtype='float', values=test_data),
emlearn.cgen.array_declare(f"{name}_testset_results", dtype='int', values=test_res),
emlearn.cgen.constant_declare(f'{name}_testset_features', val=len(feature_columns)),
emlearn.cgen.constant_declare(f'{name}_testset_samples', val=len(test_predictions)),
])
test_code = test_dataset + \
f'''
#include "{model_filename}" // emlearn generated model
#include <stdio.h> // printf
int
{name}_test() {{
const int n_features = {name}_testset_features;
const int n_testcases = {name}_testset_samples;
int errors = 0;
for (int i=0; i<n_testcases; i++) {{
const float *features = {name}_testset_data + (i*n_features);
const int expect_result = {name}_testset_results[i*1];
const int32_t out = model_predict(features, n_features);
if (out != expect_result) {{
printf(\"test-fail sample=%d expect=%d got=%d \\n\", i, expect_result, out);
errors += 1;
}}
}}
return errors;
}}
int
main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{{
const int errors = {name}_test();
return errors;
}}'''
test_source_file = os.path.join(out_dir, f'test_{name}.c')
with open(test_source_file, 'w') as f:
f.write(test_code)
print('Generated', test_source_file)
include_dirs = [ emlearn.includedir ]
test_executable = emlearn.common.compile_executable(
test_source_file,
out_dir,
name='test_{name}',
include_dirs=include_dirs
)
import subprocess
errors = None
try:
subprocess.check_output([test_executable])
errors = 0
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
errors = e.returncode
Plotting tools
Plots the decision boundaries score landscape
def plot_results(ax, model, X, y):
from sklearn.inspection import DecisionBoundaryDisplay
# show classification boundaries
DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator(
model, X, alpha=0.4, ax=ax, response_method="auto",
)
# show datapoints
ax.scatter(X.iloc[:, 0], X.iloc[:, 1], c=y, s=20, edgecolor="k")
Train, convert and run model
Using the standard scikit-learn process, and then using emlearn to convert the model to C
def build_run_classifier(ax, model, name):
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
target_column = 'target'
# Train model
test, train = train_test_split(dataset, test_size=0.3, random_state=3)
feature_columns = list(set(dataset.columns) - set([target_column]))
# limit to 2 columns to be able to visualize
feature_columns = ['total_phenols', 'color_intensity']
feature_columns = ['alcohol', 'flavanoids']
model.fit(train[feature_columns], train[target_column])
out_dir = os.path.join(here, 'classifiers')
if not os.path.exists(out_dir):
os.makedirs(out_dir)
model_filename = os.path.join(out_dir, f'{name}_model.h')
cmodel = emlearn.convert(model, method='loadable')
code = cmodel.save(file=model_filename, name='model')
test_pred = cmodel.predict(test[feature_columns])
# Generate a test dataet
test_data = numpy.array(test[feature_columns]).flatten()
errors = check_correctness(out_dir, name, model_filename, test_data, test_pred, feature_columns)
print(f"Tested {name}: {errors} errors")
plot_results(ax, model, test[feature_columns], test[target_column])
Classifiers to compare
Some of the supported modela and configurations
import sklearn.ensemble
import sklearn.tree
import sklearn.neural_network
import sklearn.naive_bayes
classifiers = {
'decision_tree': sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(),
'random_forest': sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10, random_state=1),
'extra_trees': sklearn.ensemble.ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=10, random_state=1),
'gaussian_naive_bayes': sklearn.naive_bayes.GaussianNB(),
'sklearn_mlp': sklearn.neural_network.MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(10,10,), max_iter=1000, random_state=1),
}
Run all classifiers
def main():
fig, axs = plt.subplots(
ncols=1,
nrows=len(classifiers),
figsize=(4, 4*len(classifiers)),
sharex=True, sharey=True,
)
for ax, (name, cls) in zip(axs, classifiers.items()):
build_run_classifier(ax, cls, name)
ax.set_title(name)
if ax != axs[-1]:
ax.set_xlabel('')
plt.show()
main()
Generated /home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/emlearn/checkouts/latest/examples/classifiers/test_decision_tree.c
Tested decision_tree: None errors
Generated /home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/emlearn/checkouts/latest/examples/classifiers/test_random_forest.c
Tested random_forest: None errors
Generated /home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/emlearn/checkouts/latest/examples/classifiers/test_extra_trees.c
Tested extra_trees: None errors
Generated /home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/emlearn/checkouts/latest/examples/classifiers/test_gaussian_naive_bayes.c
Tested gaussian_naive_bayes: None errors
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/emlearn/envs/latest/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sklearn/neural_network/_multilayer_perceptron.py:691: ConvergenceWarning: Stochastic Optimizer: Maximum iterations (1000) reached and the optimization hasn't converged yet.
warnings.warn(
Generated /home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/emlearn/checkouts/latest/examples/classifiers/test_sklearn_mlp.c
Tested sklearn_mlp: None errors
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.631 seconds)