Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Anomaly Detection comparison
Simple demonstration of Anomaly Detection methods implemented in emlearn
# Example adapted from
# "Comparing anomaly detection algorithms for outlier detection on toy datasets"
# Author: Alexandre Gramfort <alexandre.gramfort@inria.fr>
# Albert Thomas <albert.thomas@telecom-paristech.fr>
# License: BSD 3 clause
# https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/miscellaneous/plot_anomaly_comparison.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-miscellaneous-plot-anomaly-comparison-py
import os.path
import emlearn
import numpy
import pandas
import seaborn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#matplotlib.rcParams["contour.negative_linestyle"] = "solid"
try:
# When executed as regular .py script
here = os.path.dirname(__file__)
except NameError:
# When executed as Jupyter notebook / Sphinx Gallery
here = os.getcwd()
Create dataset
Using a simple multi-class dataset included with scikit-learn
def make_datasets(n_samples = 300, outliers = 0.15, seed=42):
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons, make_blobs
rng = numpy.random.RandomState(seed)
n_outliers = int(outliers * n_samples)
n_inliers = n_samples - n_outliers
# Define datasets
blobs_params = dict(random_state=0, n_samples=n_inliers, n_features=2)
datasets = [
make_blobs(centers=[[0, 0], [0, 0]], cluster_std=0.5, **blobs_params)[0],
make_blobs(centers=[[2, 2], [-2, -2]], cluster_std=[0.5, 0.5], **blobs_params)[0],
make_blobs(centers=[[2, 2], [-2, -2]], cluster_std=[1.5, 0.3], **blobs_params)[0],
4.0
* (
make_moons(n_samples=n_samples, noise=0.05, random_state=0)[0]
- numpy.array([0.5, 0.25])
),
#14.0 * (numpy.random.RandomState(42).rand(n_samples, 2) - 0.5),
]
def add_outliers(X):
return numpy.concatenate([X, rng.uniform(low=-6, high=6, size=(n_outliers, 2))], axis=0)
datasets = list(map(add_outliers, datasets))
return datasets
outliers_fraction = 0.15
datasets = make_datasets(outliers=outliers_fraction)
Models to compare
from sklearn.covariance import EllipticEnvelope
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
from sklearn.mixture import GaussianMixture, BayesianGaussianMixture
anomaly_algorithms = [
("Elliptic Envelope", EllipticEnvelope(contamination=outliers_fraction)),
("GMM (2, full)", GaussianMixture(n_components=2, covariance_type='full')),
("GMM (4, full)", GaussianMixture(n_components=4, covariance_type='full')),
#("Gaussian Mixture model (32, full)", GaussianMixture(n_components=4, covariance_type='diag', random_state=1)),
("Baysian GMM ", BayesianGaussianMixture(n_components=12,
covariance_type='diag', random_state=1, n_init=4,
degrees_of_freedom_prior=1.1, max_iter=20)
),
# Not yet supported
#( "Isolation Forest", IsolationForest(contamination=outliers_fraction, random_state=42)),
#("One-Class SVM", svm.OneClassSVM(nu=outliers_fraction, kernel="rbf", gamma=0.1)),
]
Plotting tools
Plots the anomaly score landscape
def plot_results(ax, model, X):
res = 20
xx, yy = numpy.meshgrid(numpy.linspace(-7, 7, res), numpy.linspace(-7, 7, res))
try:
y_pred = model.score_samples(X)
Z = model.score_samples(numpy.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
except FloatingPointError as e:
print(e)
return
# Normalize the anomaly scores to 0.0 -> 1.0
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
def nomalize_score(s, fit=False):
s = -1.0 * s.reshape(-1, 1)
if fit:
scaler.fit(s)
return scaler.transform(s)[:,0]
Z = nomalize_score(Z, fit=True)
y_pred = nomalize_score(y_pred, fit=True)
cmap = seaborn.color_palette("rocket", as_cmap=True)
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=numpy.linspace(0.0, 1.0, 5), linewidths=0.6, colors="black")
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cmap)
# Plot datapoints
seaborn.scatterplot(ax=ax, x=X[:, 0], y=X[:, 1], s=10, hue=y_pred, palette=cmap, legend=False)
ax.set_xlim(-7, 7)
ax.set_ylim(-7, 7)
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
Run comparison
fig, axs = plt.subplots(
ncols=len(anomaly_algorithms),
nrows=len(datasets),
figsize=(len(anomaly_algorithms) * 2 + 4, 12.5),
sharex=True, sharey=True,
)
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.02, right=0.98, bottom=0.001, top=0.96, wspace=0.05, hspace=0.01)
for i_dataset, X in enumerate(datasets):
for i_algorithm, (name, model) in enumerate(anomaly_algorithms):
# Train model
print(f"Trying {name}")
try:
model.fit(X)
except FloatingPointError as e:
print(e)
continue
# Convert to C
cmodel = emlearn.convert(model, method='inline')
# Visualize output
ax = axs[i_dataset, i_algorithm]
plot_results(ax, cmodel, X)
if i_dataset == 0:
ax.set_title(name, size=18)
plt.show()
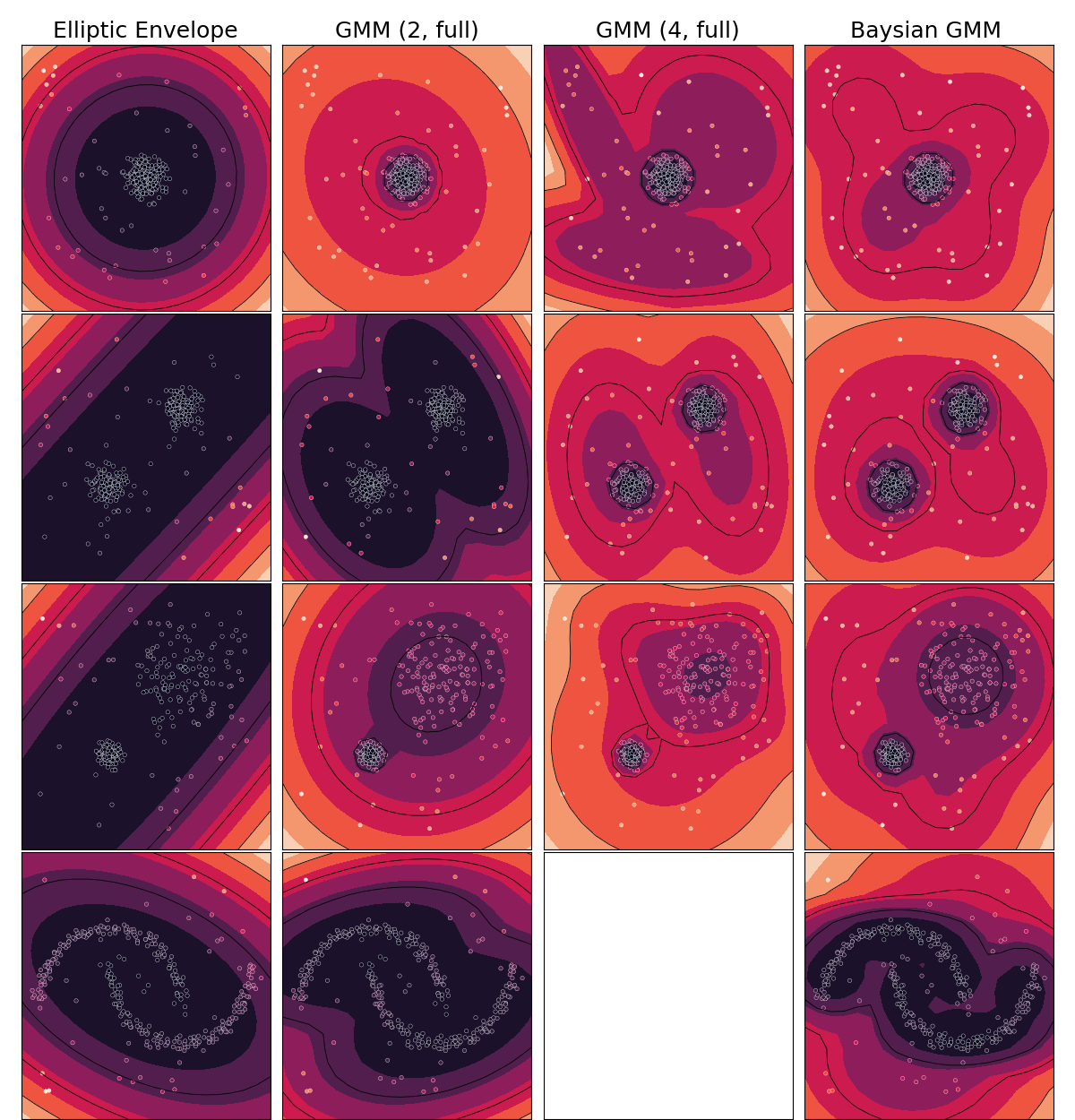
Trying Elliptic Envelope
Trying GMM (2, full)
Trying GMM (4, full)
Trying Baysian GMM
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/emlearn/envs/latest/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sklearn/mixture/_base.py:268: ConvergenceWarning: Initialization 4 did not converge. Try different init parameters, or increase max_iter, tol or check for degenerate data.
warnings.warn(
Trying Elliptic Envelope
Trying GMM (2, full)
Trying GMM (4, full)
Trying Baysian GMM
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/emlearn/envs/latest/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sklearn/mixture/_base.py:268: ConvergenceWarning: Initialization 4 did not converge. Try different init parameters, or increase max_iter, tol or check for degenerate data.
warnings.warn(
Trying Elliptic Envelope
Trying GMM (2, full)
Trying GMM (4, full)
Trying Baysian GMM
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/emlearn/envs/latest/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sklearn/mixture/_base.py:268: ConvergenceWarning: Initialization 4 did not converge. Try different init parameters, or increase max_iter, tol or check for degenerate data.
warnings.warn(
Trying Elliptic Envelope
Trying GMM (2, full)
Trying GMM (4, full)
underflow encountered in exp
Trying Baysian GMM
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/emlearn/envs/latest/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sklearn/mixture/_base.py:268: ConvergenceWarning: Initialization 4 did not converge. Try different init parameters, or increase max_iter, tol or check for degenerate data.
warnings.warn(
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 53.706 seconds)